International Journal of Anatomical Sciences 2013, 4(1):3-8
Research Paper
Profunda Femoris Artery and its Branching Pattern and Variations
Eswari AK, Hemanth Kommuru, Satyalakshimi V, Swayam Jothi S.
Department of Anatomy, Shri Sathya Sai Medical College & Research Institute, Ammapettai, Nellikuppam – 603 108, Tamil Nadu, India.
Key words: Profunda femoris artery, Variations, Medial circumflex artery, Lateral circumflex artery &
Perforators
Abstract: Profunda femoris artery is the main artery of the posterior compartment of thigh. 40 adult specimens and 10 foetal specimens were dissected and the level of origin of Profunda femoris artery in adult cadavers varied from 2 cms to 9 cms from midpoint of inguinal ligament and 0.8 cms to 1 cms in fetuses. In the adult in 4 specimens Lateral circumflex femoral artery was arising from Femoral artery, and in 5 specimens Medial circumflex was arising from Femoral artery & out of 10 fetus specimens in 8 specimens Medial & Lateral circumflex femoral arteries were arising from the Femoral artery and in two specimens from the Profunda femoris artery. All the Perforating arteries were arising from Profunda femoris except in 1 adult specimen where the second perforator was arising from Femoral artery. Profunda femoris artery is an important large branch of Femoral artery taking part in the longitudinal anastomoses at the back of the thigh. Thorough knowledge about the normal course and the variations of Arteria profunda femoris is essential for the vascular and orthopaedic surgeons and hence a detailed study of this artery was undertaken.
Profunda femoris artery (deep femoral artery) is an important large branch of femoral artery 3.5 cm distal to the taking part in the longitudinal anastomoses at the back of the thigh. Since superficial femoral artery occlusion is more common, surgical exposure of the Profunda femoris artery is often necessary in vascular reconstructive procedures. Management of groin sepsis involving the Femoral artery requires removal of infected tissue or prosthetic material and restoration of blood flow in many cases through the Profunda femoris artery.
The knowledge about the normal Profunda femoris artery and its variations are very important for the vascular surgeon according to which he can modify the surgical procedure in a more satisfactory way. This will help him to prevent most of the common post operative complications. A thorough knowledge about the normal course and its variations were essential.
Hence a detailed study of the profunda femoris artery and its variations in the branching pattern was undertaken.
Materials and Methods
40 thigh specimens from adult human cadavers and 10 thigh specimens from dead born fetuses were made use of. Conventional dissection method was used for the study
Observations
Observations were made under the following headings:
i. The level of origin of profunda femoris artery from the midpoint of inguinal ligament.
ii. Relation of origin of profunda femoris artery to femoral artery
iii. Branches
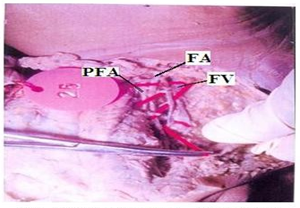
The distance of origin of the profunda femoris artery from the midpoint of the inguinal ligament ranged from 0.2 to 9 cm with an average 3.88 cm in adult cadavers (Table 1). In 36 specimens the distance of the origin of the profunda femoris artery from the midpoint of the inguinal ligament was less than 3.88 cm & in four specimens it was more than 3.88 cm (Table 2)(Fig.1).
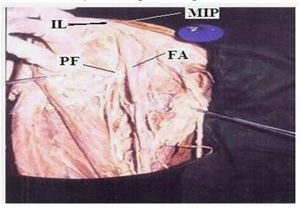
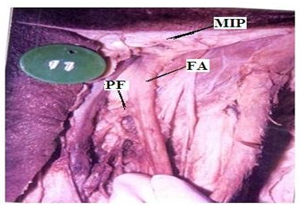
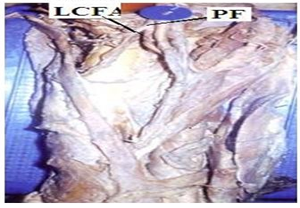
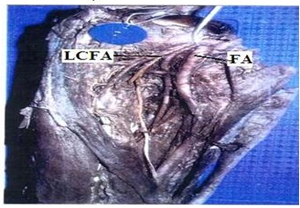
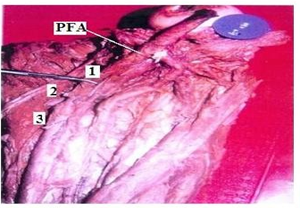
In the dead born fetuses the origin of the Profunda femoris artery from the midpoint of the inguinal ligament ranged from 0.80 to 1.00cms with an average of 0.94 cm in length (Table 3) (Fig. 2). In four specimens origin of Profunda femoris from the midpoint of the inguinal ligament was less than 0.94 cm and in 6 specimens it was more than 0.94 cm. 38(95%) out of 40 adult specimens had the normal posterolateral origin (Fig. 3) and two (5%) of them had a more lateral origin (Fig. 4) (Table 4) from the femoral artery.
In all the 10 fetus specimens the profunda femoris artery was arising from the lateral side of the Femoral artery.
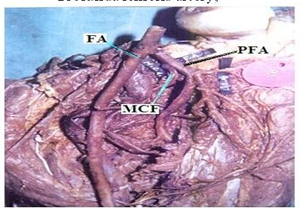
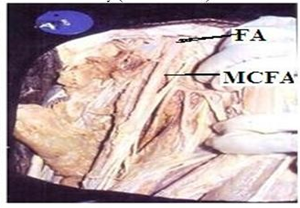
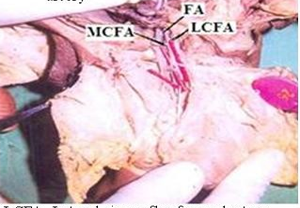
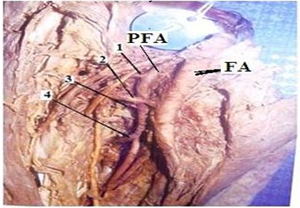
Regarding the branches, in 35(87.5%) out of 40 specimens of adult cadavers the Medial circumflex femoral artery was arising from the posteromedial side of the profunda femoris artery (Fig. 5). In 5(12.5%) specimens it was arising directly from the Femoral artery (Fig. 6) (Table 5). In 36(90%) out of 40 specimens Lateral circumflex femoral artery was arising from the profunda femoris artery (Fig. 7). In four (10%) specimens it was arising from Femoral artery (Fig. 8) (Table 6).
| ADULT CADAVERIC PRESENT STUDY | |||
| Table – 1 | |||
| DISTANCE OF ORIGIN OF PROFUNDA FERMORIS ARTERY FROM MIDPOINT OF INGUINAL LIGAMENT | |||
| Spec.No | Distance in cm | Spec.No | Distance in cm |
| 1 | 9 | 21 | 9 |
| 2 | 3.8 | 22 | 3.8 |
| 3 | 3.5 | 23 | 3.5 |
| 4 | 3.5 | 24 | 3.5 |
| 5 | 3.6 | 25 | 3.6 |
| 6 | 3.5 | 26 | 3.5 |
| 7 | 2 | 27 | 2 |
| 8 | 3.6 | 28 | 3.6 |
| 9 | 3.6 | 29 | 3.6 |
| 10 | 3.7 | 30 | 3.7 |
| 11 | 6 | 31 | 6 |
| 12 | 3.5 | 32 | 3.5 |
| 13 | 3.5 | 33 | 3.5 |
| 14 | 3.7 | 34 | 3.7 |
| 15 | 3.4 | 35 | 3.4 |
| 16 | 3.6 | 36 | 3.6 |
| 17 | 3.5 | 37 | 3.5 |
| 18 | 3.6 | 38 | 3.6 |
| 19 | 3.5 | 39 | 3.5 |
| 20 | 3.5 | 40 | 3.5 |
| Average Length : 3.88cm | |||
| VARIABLES | SPECIMENS IN NUMBERS | PERCENTAGE |
| less than 3.88cms | 36 | 90% |
| more than 3.88 cms | 04 | 10% |
Table – 2
| DISTANCE OF ORIGIN OF PFA FROM INGUINAL LIGAMENT | |
| AVERAGE DISTANCE = 3.88cms | |
| DISTANCE | PERCENTAGE |
| less than average distance | 90% |
| more than average distance | 10% |
In 2(20%) out of 10 fetus specimens the Lateral & Medial circumflex femoral arteries were arising the Femoral artery (fig 9) and in the rest of the eight specimens (80%) they were arising from the Profunda femoris artery.
Table – 3
| Fetal cadaveric present study | ||
| Distance of origin of profunda femoris artery from the inguinal ligament | ||
| Spec.No | Distance in cm | |
| 1 | 0.9 | |
| 2 | 1.0 | |
| 3 | 0.8 | |
| 4 | 1.0 | |
| 5 | 1.0 | |
| 6 | 0.9 | |
| 7 | 1.0 | |
| 8 | 0.8 | |
| 9 | 1.0 | |
| 10 | 1.0 | |
| Average Length : 0.94cm | ||
| Variable | Specimen in number | Percentage |
| Less than 0.94cm | 4 | 40% |
| More than 0.94cm | 6 | 60% |
In 34 (85%) specimens the Lateral circumflex femoral artery gave three branches – ascending, transverse & descending (Fig. 7, 8). In 6 (15%) speci- mens four branches were arising – 1 ascending, 2 transverse and 1 descending (Table 7) (Fig. 10).
Table 4