International Journal of Anatomical Sciences 2011, 2(2): 22-25
Research Paper
Duplication of Great Saphenous Vein in South Indian Population
Udhaya K, Sarala Devi KV, Sridhar J, Melani Rajendran S.
Department of Anatomy, Vinayaka Mission Kirupananda Variyar Medical College, Salem 636 308, Tamilnadu, India.
Department of Surgery, Vinayaka Mission Kirupananda Variyar Medical College and Hospital, Salem 636 308, Tamilnadu, India.
Department of Anatomy, Sri Ramachandra Medical College, Chennai 600 117, Tamilnadu, India
Key words : Great Saphenous vein, Duplication, Varicose veins.
Abstract: The great saphenous vein is the conduit of choice as a graft in coronary artery bypass arterial reconstruction and for valvuloplasty in medical and surgical practice. The great saphenous vein is also used for bypass obstructions in case of atheromatous occlusion of the femoral and coronary arteries. The duplication of great saphenous vein is a frequent cause of failure to achieve the expected results following primary ligation for the treatment of varicose veins. The current study was therefore focussed on duplication of great saphenous vein and its incidence in South Indian population. For this purpose a total sample of 70 adult specimens of both sides, 22 male and 13 female cadavers were used. The results were analysed by dissection method. For this, the incidence is used as parameter. Duplication was observed bilaterally in one cadaver with the incidence of 3% which correlates with western population. The results conclude that precise knowledge about normal anatomy of great saphenous vein with their variations becomes mandatory for a successful clinician. The study about this fact by our Indian authors was scarce. Hence an attempt was made in the present study to find out duplication of Great saphenous vein in South Indian population.
The great saphenous vein originates from the inner part of the dorsal venous arch of the foot, by the union of medial end of dorsal venous arch and medial marginal vein. After its formation, it passes in front of the medial malleolus, single trunk lying along the posteromedial aspect of the knee joint, receiving anterior and posterior tributaries along its course, one hand breadth posterior to the patella, and then upto the fossa ovalis or saphenous opening (4 cm below and lateral to the pubic tubercle)where it enters the femoral vein (Williams et al.,2005).
The variations are more common in the upper segment of great saphenous vein, where it ends near the femoral vein. Common cause of recurrence of varicosities after high ligation and stripping are said to be failure to ligate the duplicated great saphenous vein if any (Linton, 1938; Sherman, 1944; Summers, 1953). The incidence and pattern of duplication have drawn attention to the possible role of its variation as a source of recurrent varicose veins (Kosinski, 1926; Glasser, 1943; Daseler, 1946; Haeger,1977;Corrales,2002).A thorough and effective knowledge of the anatomical variations of the great saphenous vein like duplication, determines the good results of medical and surgical management.
Materials and Methods
The study was conducted in seventy adult specimens of both sides including 22 male and 13 female cadavers of age group 40 to 60 years, over a period of three years, in the department of Anatomy, Sri Ramachandra Medical College & Research Institute, Chennai. By dissection method, the course of great saphenous vein from the medial malleolus to the sapheno-femoral junction in both legs, the duplication of great saphenous vein with their termination into femoral vein and its tributaries were traced.
Observations
Out of 70 specimens dissected (Table-1), in 68, the great spahenous vein was seen normal (Fig. 1) and the duplication of the great saphenous vein was observed only in one male cadaver bilaterally (Fig. 2 and 3). In the duplicated vein, the level of termination and their drainage pattern along with their terminal tributaries were noted separately for both sides. On both sides of a male cadaver, the duplicated vein was found to terminate into the femoral vein. On the right side, the distance measured between the anterior superior iliac spine and sapheno- femoral junction was 9.7 cms and on the left side it was 10.1 cms. The sapheno-femoral junction was found to be 4.2 cms lateral to pubic tubercle on the right side and 4.5 cms lateral to pubic tubercle on the left side.
| Sex | No ofCadavers | No ofSpeci-mens | Duplica-tion | Normal |
| Male | 22 | 44 limbs | 2 limbs | 42 limbs |
| Female | 13 | 26 limbs | – | 26 limbs |
| Total | 35 | 70 limbs | 2 limbs | 68 limbs |
Table-1 Details of cadaver samples studied for great saphenous vein
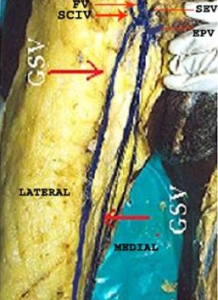
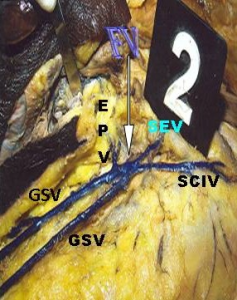
On observing the drainage pattern of the right side, the duplicated great saphenous vein on the lateral part of the thigh drained into the femoral vein at the fossa ovalis along with the superficial circumflex iliac vein whereas the duplicated vein observed on the medial part of the right side drained into the femoral vein at the fossa ovalis along with the external pudendal vein and superficial epigastric vein (Fig. 2) Similarly on the left side, the medially observed duplicated vein drained into the femoral vein at the fossa ovalis along with the external pudendal vein whereas the laterally observed duplicated vein on the left side drained into the femoral vein at the fossa ovalis along with the superficial circumflex iliac vein and superficial epigastric vein (Fig. 3) No other abnormalities were detected in the specimen other than duplication. The remaining 68 specimens showed normal course and pattern of great saphenous vein without any duplication.
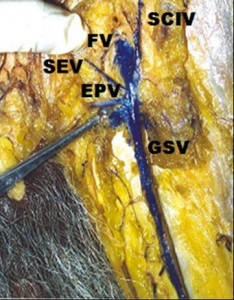
Fig. 1 Normal great saphenous vein
(FV-Femoral vein;SCIV – Superficial circumflex iliac vein;SEV-Superficial epigastric vein;EPV- External pudendal vein;GSV-Great saphenous vein)
Discussion
The great saphenous vein has an important role as autograft for arterial by- pass surgery (Shah et al., 1986). A proper understanding of the anatomy of the super- ficial veins is elementary for improving the results of operative treatment. Duplications of great saphenous vein are often demon- strated by dissection during arterial bypass surgery.
Fig. 2 Duplication of great saphenous vein on right side (FV-Femoral vein;SCIV-Superficial circumflex iliac vein;SEV-Superficial epigastric vein;EPV-External pudendal vein;GSV-Great saphenous vein).
Fig. 3 Duplication of great saphenous vein on left side (FV-Femoral vein;SCIV-Superficial circumflex iliac vein;SEV-Superficial epigastric vein;EPV-External pudendal vein;GSV-Great saphenous vein)
Clinicians unfamiliar with venous insufficiency, particularly disorders of the superficial venous system like duplication, often underestimate the complexity of the problem and the importance of proper evaluation before initiating treatment. In addition to a directed history, evaluation and physical examination, additional evaluation with use of a variety of non-invasive diagnostic instruments, including duplex ultrasound, may be necessary before the treatment of varicose disease (Ricci, 1999) for determining the cause and severity. The precise anatomy of the great saphenous vein should be determined preoperatively by phlebography since this information is valuable for proper surgical planning before vein is used as a graft or for in situ bypass in the lower extremity. Phlebography (Saphenography) is a reliable method for pre-operative assessment of variations and connections of great saphenous vein especially when anteroposterior and lateral images are taken (Shah et al.1986; Veith et al., 1979).
Glasser (1943) reported and classified the venous drainage at the region of fossa ovalis into 19 sapheno-femoral drainage patterns after dissecting 50 bodies (100 limbs) and according to him duplication belongs to Type-V B which shows double great saphenous vein joining at the fossa ovalis with the incidence of 3% . In the present study (South Indian population), the duplication was found bilaterally in one male cadaver with the incidence of 3% which correlates with the study of Glasser (1943) in Western population. Similar reports and references in South Indian population regarding duplication of great saphenous vein were scarce to compare and correlate our present study. Hence many reports from South Indian population are awaited.
Conclusion
A thorough understanding of the anatomical variations of great saphenous vein is important in providing information for the vascular surgical operations concerning with lower extremity. Further studies are required involving more samples Udhaya et al. – Duplication of great saphenous vein to gather information pertaining to frequency of true duplications of the great saphenous vein in Indian population.
References
Corrales,N.E.,Irvine,A.,McGuinness,C.L.,Dourado,R and Burnand, K.G. Incidence and pattern of long saphenous vein duplication and its possible implications for recurrence after varicose vein surgery. British Journal of Surgery, 89: 323-326, 2002.
Daseler, E.H., Anson, B.J., Reimann, A.F., Beaton, L.E. The saphenous venous tributaries and related structures in relation to the technique of high ligation. Based chiefly upon a study of 550 anatomical dissections. Surg Gynecol Obstet.82: 53-63, 1946.
Glasser, S.T. An anatomic study of the venous variations at the fossa ovalis. The significance of recurrences following ligations. Arch Surg.46: 289-95, 1943.
Haeger, K. The anatomy of the veins of the leg. In: Hobbs JT, Edition. The treatment of Venous Disorders. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: JB Lippincott, 1977.
Kosinski, C. Observations on the superficial venous system of the lower extremity. J Anat. 60: 131-42, 1926.
Linton, R.R. The communicating veins of the lower leg and the operative technic for their ligation. Ann Surg. 107: 582, 1938.
Ricci,S. Caggiati,A. Does a double long saphenous vein exist? Phlenbology. 14: 59-64, 1999.
Shah, D.M., Chang, B.B., Leopold,P.W, Corson, J.D., Leather, R.P., Karmody, A.M. The anatomy of the great saphenous venous system. J Vasc Surg. 3: 273-83, 1986.
Sherman,R.S. Varicose Veins: Anatomic findings and an operative procedure based up the duplication of great saphenous vein on them. Ann Surg.120: 772, 1944.
Summers, J.E. Highlights in the treatment of varicose veins and ulcers. Am J Surg 86: 443, 1953.
Veith,F.J., Moss,C.M., Sprayregen,S., Montefusco,C.
Preoperative saphenous venography in arterial reconstructive surgery of the lower extremity. Surgery. 85: 253-6, 1979.
Williams et al. In Henry Gray Text book of Anatomy; 39th Edition, 145, Published by Elseiver Churchill Livingstone, 2005.